Introduction
Systemic Lupus Erythematous (SLE) is an Autoimmune disease that can affect any part of the body. Here the immune system attacks the body’s cells & tissues, resulting in inflammation & tissue damage.
It is Chronic, Unpredictable & characterized by exacerbations & remissions.
Incidence- In India 3.2 per 1, 00,000 population. More than 85% are females (Female: Male=9:1)
It commonly occurs in Age group 20-50 yrs.
Etiology: Unknown
Most probable causes:
- Genetic influence -HLA B8, DR3, DR2 Inherited complement deficiencies
- Hormones – Oestrogen imbalance
- Environmental factors – UV light, Physical & emotional stress, Infections
- Abnormal immune system
- Certain medications
Pathogenesis:
Important stages of SLE
- Immune insufficiency stage
- Hyper activation stage
- Formation of Auto antibodies & Immune complexes stage
- Active disease stage
- Destruction stage
Clinical manifestations:
- Ranges from a relatively mild disorder to rapidly progressing, affecting multiple body systems.
- Most commonly affects the skin/muscles, joints, lining of lungs, heart, nervous tissue and kidneys.
Constitutional symptoms:
- Fever
- Headache
- Malaise
- Weight loss
Mucocutaneous manifestations:
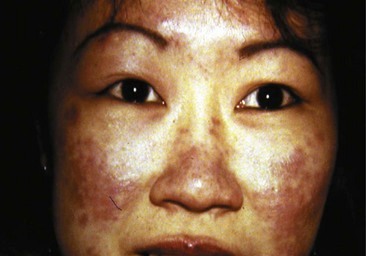
- Classical Malar rash- butterfly rash.
- Rash in pre-auricular, auricular & post auricular area.
- Diffuse hyper pigmentation/maculopapular rash.
- Discoid lesions.
- Scalp- Alopecia is common
Gastrointestinal manifestations:
- Oral ulcers
- Dysphagia
- Anorexia
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Abdominal pain
Musculoskeletal manifestations:
- Polyarthralgia with morning stiffness
- Arthritis :Commonly affected- Small joints of hands (Phalangeal & Interphalangeal), wrist joint, knee joint Erosive arthritis is rare.
Cardiopulmonary manifestations:
- Pericarditis: often silent
- Myocarditis: presents with unexplained tachycardia, heart failure, arrhythmias or heart block.
- Pleurisy & Pleural effusion: most common
- Lupus pneumonitis & alveolar hemorrhage: rare
Renal manifestations:
- Renal involvement may be asymptomatic
- Lupus nephritis- Ranging from mild proteinuria to glomerulo nephritis.
Neurological manifestations:
- Generalized/focal seizures
- Peripheral neuropathy
- Headache
- Cognitive dysfunction:-Disorientation, Memory deficits and Psychiatric symptoms.
Haematological manifestations:
- Anemia is common
- Formation of antibodies against blood cells
- Concomitant iron deficiency may be present.
- Thrombocytopenia
- Leucopenia
Criteria for diagnosis of SLE 4/11 Criteria (American College of Rheumatology):
- Serositis – heart, lung, peritoneum
- Oral ulcers – painless esp palate
- Arthritis – non-erosive
- Photosensitivity
- Blood disorders -Hemolytic anaemia, low WBC count, low platelet count
- Renal involvement – proteinuria /± casts
- ANA
- Immunologic phenomena – LE cells, anti-dsDNA Ab, anti-Sm Ab, antiphospholipid Ab,
- Neurological disorders – seizures/ psychosis
- Malar rash – cheeks + nasal bridge
- Discoid rash
Diagnostic Tests
- CBC – Hematological problems
- ESR & CRP – Indicative of Inflammatory activity
- Urine Analysis – Lupus Nephritis
- X-rays of affected joints
- Chest X-ray & CT – Pulmonary problems
- ECG – Cardiac manifestations
- CT or MRI of Brain – Neurological changes
Autoantibody tests used in SLE:
- Antinuclear antibodies (ANA) : Best Screening test,95%
- Antibodies to double-stranded (anti-dsDNA) : High specificity test,70%
- Anti-Smith antibodies (anti-Sm) : Best Confirmatory test,30%
Prognosis:
Prognosis is improved with:
- Earlier diagnosis
- Earlier and better treatment regimens
- Careful monitoring for organ involvement
General Principles
- Sun avoidance & use of high factor sun-blocks
- Lifestyle modifications
Eg.: Exercise
Smoking avoidance
Stress management etc.
Ayurvedic perspective
SLE is a multi system disorder- ‘Vyadhi Sankara’. Few signs and symptoms can be correlated with Vatarakta or amavata.
Management of SLE in Ayurveda:
- Nidana parivarjana
- Apatarpana
- Vataraktavat chikitsa
- to dhatu
- Bahirparimarjana chikitsa
- Shamana aushadhi
- Rasayana prayoga
Deepana Pachana yogas
- Amritadi Kashaya
- Agnikumara Rasa
- Amrutottara Kashaya
- Shunthi Jala
- Chitrakadi vati
- Ajamodadi Choorna
Vatarakta chikitsa prayoga:
- Uttana Vatarakta- Alepa, Abhyanga, Parisheka, Upanaha
- Gambhira vatarakta- Virechana, Niruha basti, Snehapana
Basti:
- Erandamooladi Niruha Basti
- Kshara Basti
- Dashamooladi Niruha Basti
- Madhuyashtyadi Niruha Basti
- Balaguduchyadi Niruha Basti
- Vaitarana basti
Alepa:
- Eladi Choorna
- Nimbadi Choorna
- Patoladi Choorna
- Manjishtadi Lepa
- Sarshapadi Lepa
Abhyanga
- Madhuyashti taila
- Pinda taila
Swedana
Parisheka Sweda, Pinda sweda and upanaha sweda
Shamana aushadis:
- Yogaraja Guggulu – Guduchi Kashaya as Anupana
- Mahayogaraja Guggulu
- Kaishora Guggulu
- Gokshuradi Guggulu
- Maharasnadi Kwatha
- Rasnapanchaka Kwatha
- Rasnasaptaka Kwatha
- Dashamoola Kwatha
- Guggulu Tiktaka kashaya
Rasayana prayoga:
- Amrita Bhallataka Rasayana
- Madhusnuhi Rasayana
- Vardhamana Pippali Rasayana
- Swarna Mahayogaraj guggulu
- Guduchi
Author:
Dr. Keerthi Shetty
Ayurveda Doctor
Panchakarma Expert